Clock Synchronization
The chrony software ( https://chrony-project.org/ ) is used for time synchronization. Time synchronization does not require any configuration by the user.
chrony automatically selects the best or most accurate time source available and uses this to correct the local time.
The available sources can be displayed with chronyc sources:
chrony uses the GPS receiver (if available) and a pool of NTP servers from the Internet.
The chronyc tracking command can be used to view the quality of the source:
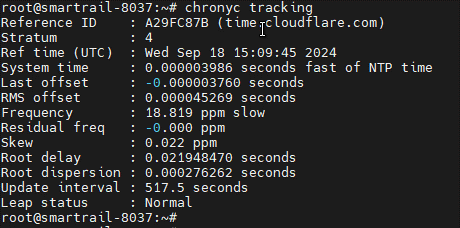
The following output from chronyc tracking means that chrony has not yet been able to receive / synchronize the time:
root@smartrail-8037:~# chronyc tracking
Reference ID : 00000000 ()
Stratum : 0
Ref time (UTC) : Thu Jan 01 00:00:00 1970
System time : 0.000000000 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : +0.000000000 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000000000 seconds
Frequency : 0.000 ppm slow
Residual freq : +0.000 ppm
Skew : 0.000 ppm
Root delay : 1.000000000 seconds
Root dispersion : 1.000000000 seconds
Update interval : 0.0 seconds
Leap status : Not synchronized
GPS
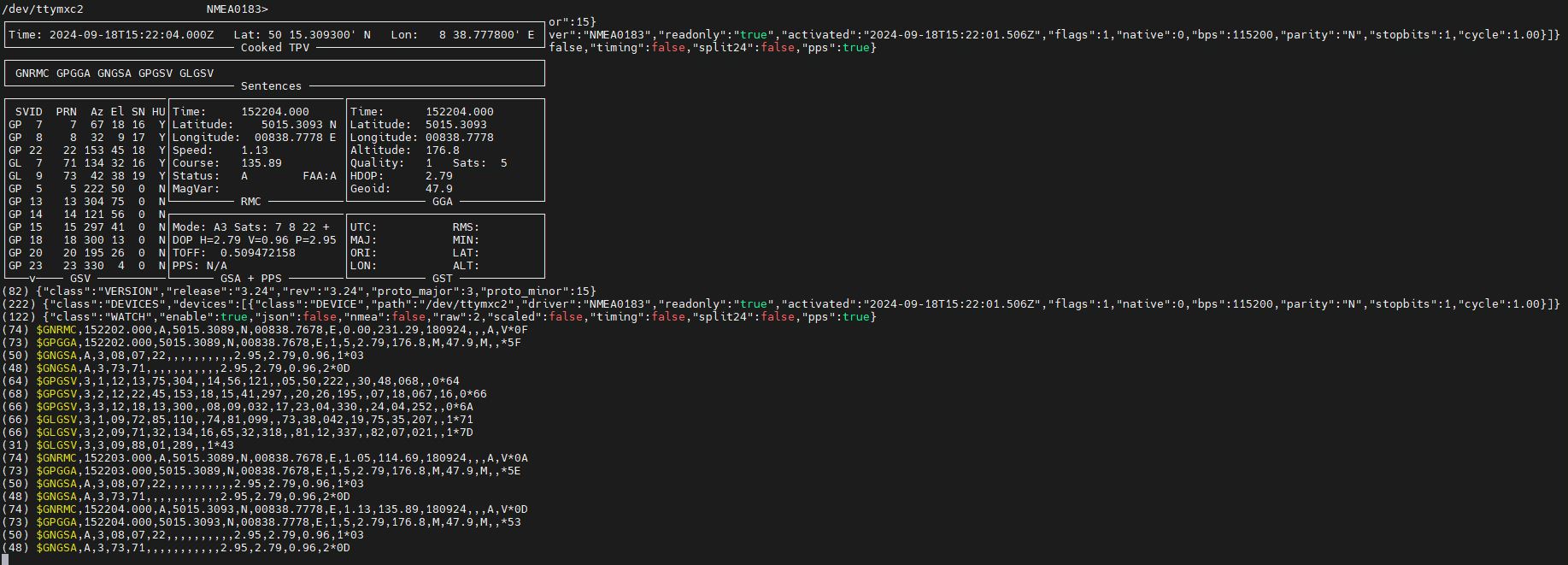
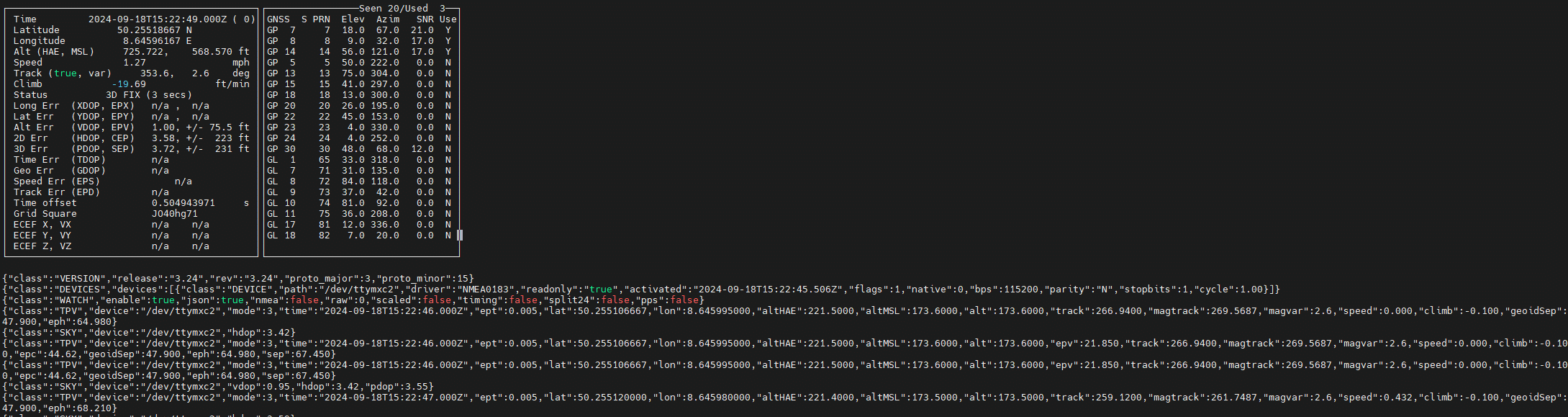
There are several command line tools for diagnosing the GPS signal, which display the information from the GPSd Deamon ( https://gpsd.gitlab.io/gpsd/ ) in different ways. Each tool continuously outputs information until it is terminated with CTRL+C or CTRL+C.
gpsmon
cgps
gpscsv
NTP server
chrony makes the time available to other participants in the local network on UDP port 123 via the NTP protocol.
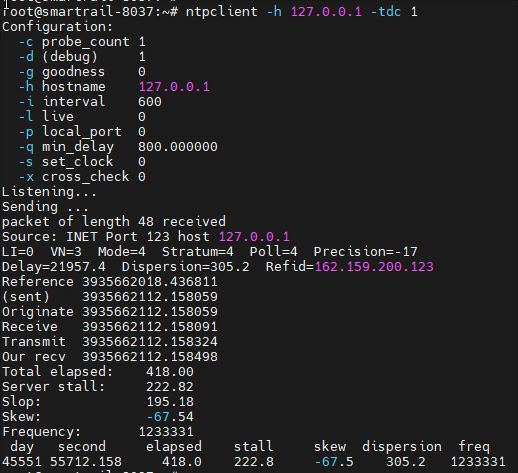
As a test, you can query your own time with the call ntpclient -h 127.0.0.1 -tdc 1: